Enterprise resource planning serves as the backbone of modern business operations, allowing organizations to streamline processes and maximize efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, ERP systems have adapted, reflecting the changing needs of businesses across various industries. This powerful software integrates core functions such as finance, HR, and supply chain management into a cohesive platform, enabling real-time data access and informed decision-making.
Throughout the years, ERP has transformed significantly, driven by advancements in technology and the growing complexity of business environments. From rudimentary solutions to sophisticated cloud-based systems, enterprise resource planning has become an essential tool for companies aiming to improve their operational capabilities.
The Evolution of Enterprise Resource Planning Systems Over the Years

The journey of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems has been a remarkable transformation, evolving from basic material requirements planning (MRP) systems in the 1960s to sophisticated, integrated solutions that streamline operations across entire organizations today. This evolution reflects not only technological advancements but also the changing landscape of business needs and practices.In the early days, traditional MRP systems were primarily focused on manufacturing, helping businesses manage inventory levels and production schedules.
As the 1980s approached, organizations began recognizing the importance of integrating various functions, leading to the emergence of Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II). MRP II expanded the focus beyond materials to include aspects such as financials and human resources, laying the groundwork for what we now know as ERP.The 1990s marked a significant turning point with the introduction of ERP systems that aimed to provide a comprehensive suite of applications to manage all facets of business operations.
Companies like SAP and Oracle became pioneers in this space, offering solutions that integrated finance, supply chain, and customer relationship management into a single system. This integration was pivotal, as it allowed organizations to streamline processes, enhance data accuracy, and improve decision-making capabilities.
Technological Advancements Influencing ERP Evolution
The evolution of ERP systems has been greatly influenced by several technological advancements. Key innovations that have shaped modern ERP solutions include:
- Cloud Computing: The shift to the cloud has facilitated greater accessibility, scalability, and flexibility for businesses, allowing them to implement ERP systems without heavy upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
- Mobile Technology: Mobile applications have enabled users to access ERP functionalities on-the-go, enhancing productivity and real-time decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning capabilities have been integrated into ERP systems, providing predictive analytics and automated processes that can help organizations forecast trends and streamline operations.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices have enhanced data collection and monitoring, allowing ERPs to provide real-time insights into operations, inventory levels, and equipment health.
These advancements reflect a shift towards greater efficiency and a focus on real-time data, empowering businesses to respond quickly to changes in the market.
Business Needs Shaping ERP Features Over Time
The dynamic nature of business requirements has continuously influenced ERP features and functionalities. As industries evolve, ERP systems have adapted to meet the specific needs of various sectors. Here are some notable trends:
- Customization: Businesses have increasingly demanded tailored solutions that fit their unique processes, leading to flexible ERP systems that can be configured to specific industry needs.
- User Experience: As user interface design became more essential, ERP vendors focused on creating intuitive interfaces that enhance usability and employee engagement.
- Regulatory Compliance: With growing regulations across industries, ERP systems have integrated compliance features to help companies adhere to standards effortlessly.
- Collaboration Tools: The rise of remote work and global teams has necessitated the inclusion of collaboration tools within ERP systems, facilitating seamless communication across departments and locations.
The evolution of ERP systems is a testament to how technological advancements and changing business needs have collaborated to create robust solutions that drive efficiency and strategic decision-making in organizations.
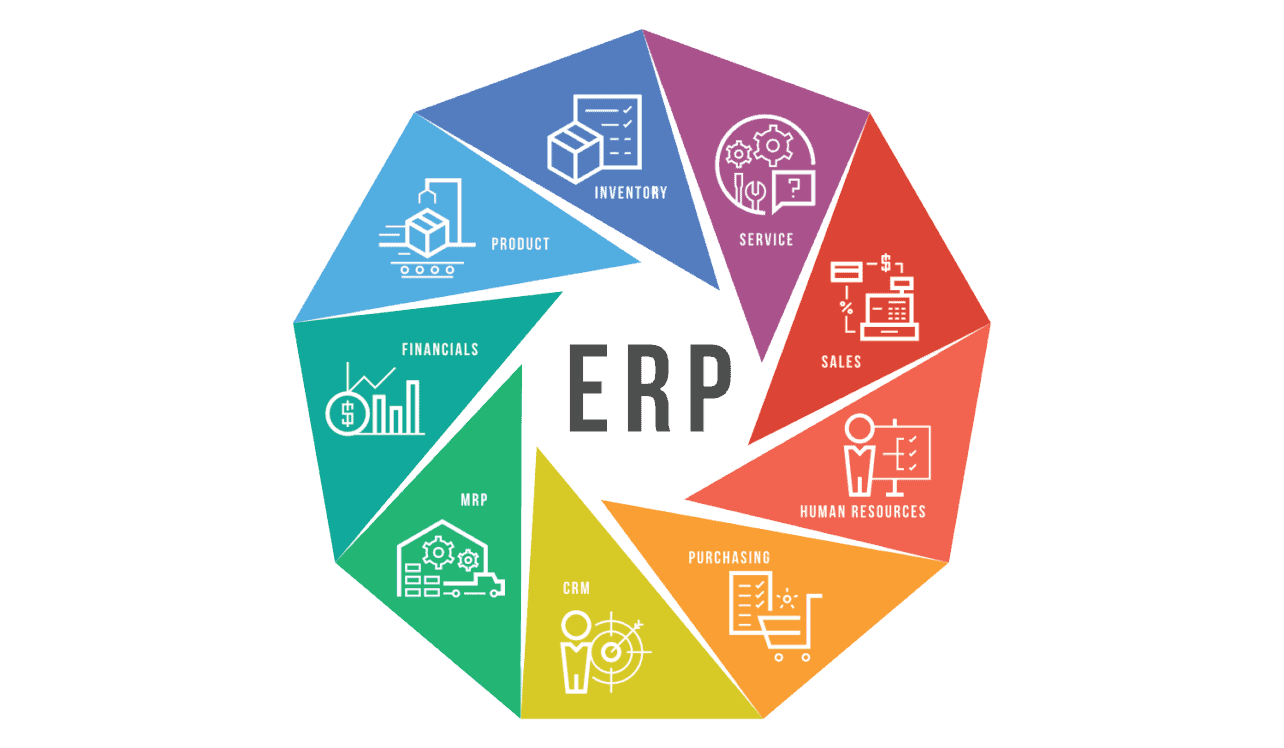
Key Components of an Enterprise Resource Planning System
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems serve as the backbone of many organizations, integrating various functions into a unified system to streamline processes and information across the enterprise. Understanding the key components of these systems can help organizations leverage their full potential. Here, we will explore the primary modules of an ERP system, the significance of data integration, and the impact of user interfaces on user experience.
Primary Modules of ERP Systems
ERP systems are built around various modules that cater to different business processes. Each module provides specialized functionalities that contribute to the overall efficiency of the organization. Here are four primary modules commonly found in ERP systems:
- Finance and Accounting: This module manages financial transactions, budgeting, forecasting, and reporting. It helps organizations maintain accurate financial records and ensures compliance with regulations.
- Human Resources (HR): The HR module is designed to manage employee records, recruitment, payroll, performance evaluation, and benefits administration. This module streamlines HR processes, enhancing employee management.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): The SCM module oversees inventory management, procurement, order fulfillment, and logistics. It helps in optimizing the supply chain, reducing costs, and improving service levels.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): This module focuses on managing customer interactions, sales tracking, and service delivery. It aids in improving customer satisfaction and fostering stronger client relationships.
Importance of Data Integration within ERP Solutions
Data integration is a crucial aspect of ERP systems, allowing disparate data sources to be unified into a single, coherent framework. This integration ensures that all departments have access to real-time data, which promotes informed decision-making and enhances operational efficiency. The benefits of data integration include:
- Improved Data Accuracy: Consolidating data from multiple sources reduces the risk of errors and discrepancies, leading to more reliable reporting and analysis.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Integrated data allows various departments to work together more effectively, as everyone has access to the same information.
- Streamlined Processes: With integrated systems, businesses can automate workflows, reducing manual data entry and increasing productivity.
- Better Compliance and Reporting: Centralized data makes it easier to adhere to regulatory requirements and generate accurate reports for stakeholders.
Role of User Interfaces in Enhancing User Experience
The user interface (UI) of an ERP system plays a pivotal role in its overall usability and effectiveness. A well-designed UI can significantly enhance the user experience, making it easier for employees to navigate the system and perform their tasks efficiently. Key aspects of user interfaces in ERP systems include:
- Intuitive Design: A clear and logical layout helps users quickly find the information and tools they need, minimizing training time and increasing adoption rates.
- Customizability: A flexible UI allows users to tailor their dashboards and workflows according to their specific roles and preferences, enhancing their interaction with the system.
- Mobile Accessibility: Modern ERPs often feature mobile-compatible interfaces, enabling users to access the system remotely, thereby supporting on-the-go decision-making.
- Visual Analytics: Incorporating data visualization tools in the UI allows users to quickly interpret complex data sets, facilitating prompt and informed decisions.
“A user-friendly interface can transform the way employees interact with an ERP system, driving greater engagement and productivity.”
Benefits of Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning Solution
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system offers numerous advantages that can significantly enhance a business’s overall performance. By integrating various functions across departments, organizations can streamline their processes, leading to improved efficiency and effectiveness in daily operations. Let’s delve into the benefits of adopting an ERP system.
Advantages of ERP Systems
The adoption of an ERP system brings a multitude of benefits to businesses, driving both operational efficiency and strategic growth. Here are five key advantages:
- Improved Data Accuracy: By centralizing all business data in one location, ERP systems reduce the risk of errors and discrepancies, ensuring that employees are always working with the most accurate information.
- Enhanced Reporting and Analytics: ERP solutions provide advanced reporting tools that allow businesses to analyze performance metrics and make more informed decisions based on real-time data.
- Streamlined Operations: With ERP, processes like order management, inventory control, and customer relationship management are integrated, leading to faster workflows and reduced operational redundancies.
- Cost Reduction: By improving efficiency and reducing manual processes, businesses can cut down on operational costs, ultimately increasing profit margins.
- Scalability and Flexibility: ERP systems can easily adapt to growing business needs, allowing for the addition of new functionalities or modules as the organization evolves.
Operational Efficiency and Productivity Improvement
ERP systems play a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency by automating routine tasks and facilitating better resource management. This automation leads to increased productivity, as employees can focus on more strategic activities rather than getting bogged down by administrative tasks. For instance, XYZ Corporation, a manufacturing company, implemented an ERP solution that automated its inventory management process. As a result, the time taken to track inventory reduced significantly, leading to less stock wastage and better order fulfillment.
Similarly, ABC Retail found that integrating their sales and customer service operations through an ERP system resulted in quicker response times to customer inquiries and complaints, boosting customer satisfaction.In both cases, these businesses experienced a noticeable uptick in productivity and operational efficiency, illustrating the transformative power of ERP integration.
Examples of Successful ERP Integration
Several organizations have successfully transformed their operations through the implementation of ERP systems, demonstrating the tangible benefits of such solutions. Notable examples include:
- Dell Technologies: Dell utilized an ERP system to streamline its supply chain management, allowing for real-time inventory tracking and improved order processing efficiency, which has contributed to its status as a leader in the technology market.
- Nike: Nike implemented an ERP solution to enhance its global operations, leading to better coordination between production and sales, ultimately resulting in increased market responsiveness and reduced lead times.
- Heinz: Heinz adopted an ERP system to manage its global manufacturing processes more effectively, which contributed to significant cost savings and improved product quality.
Challenges and Risks Associated with ERP Implementation
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system can be a transformative step for organizations aiming to streamline their operations and improve efficiency. However, it’s essential to recognize the challenges and risks that can arise during deployment, which can impact the overall success of the project. Understanding these challenges and developing strategies to mitigate their effects is crucial for a successful ERP implementation.
Common Challenges Faced During ERP Deployment
Organizations often encounter various hurdles when deploying ERP systems. Here are three prevalent challenges that can significantly affect the implementation process:
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new systems due to fear of the unknown or discomfort with new processes. This resistance can lead to decreased productivity and morale if not managed appropriately.
- Data Migration Issues: Transferring existing data to the new ERP system can be fraught with complications, including data loss, corruption, or inconsistency. Ensuring clean and accurate data is paramount for the new system to function effectively.
- Insufficient Training: When employees are not adequately trained on the new ERP system, it can lead to errors and inefficiencies. Comprehensive training programs are essential to ensure that team members can utilize the system to its full potential.
Strategies to Mitigate Risks Associated with ERP Projects
To address the risks involved in ERP implementation, organizations can adopt several strategies that pave the way for a smoother transition and successful project completion:
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Involving key stakeholders from various departments in the planning stage helps in understanding their concerns and expectations, fostering a sense of ownership in the process.
- Implement a Phased Approach: Deploying the ERP system in phases allows organizations to manage the transition gradually, making it easier to address issues as they arise and minimizing disruptions to daily operations.
- Provide Comprehensive Training and Support: Ensuring that employees receive thorough training and ongoing support can improve user adoption rates and encourage a more proficient use of the ERP system.
Impact of Organizational Culture on ERP Implementation Success
The culture within an organization plays a significant role in the success of ERP implementations. A culture that embraces change, collaboration, and continuous improvement can facilitate a smoother transition into new systems. For instance, organizations that prioritize open communication and support from leadership tend to experience higher levels of employee buy-in and lower resistance to change.
“A strong organizational culture can serve as a backbone for the successful adoption of new technologies, including ERP systems.”
Conversely, organizations with a rigid culture that resists change may struggle significantly during ERP deployment. Understanding these cultural dynamics and promoting a positive environment can minimize challenges and enhance the overall effectiveness of the ERP system once implemented.
The Role of Cloud Technology in Modern ERP Solutions: Enterprise Resource Planning
Cloud technology has transformed the landscape of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, enabling businesses to streamline their operations with enhanced efficiency and flexibility. The shift from traditional on-premises solutions to cloud-based ERP has become a pivotal change for many organizations, offering various advantages that were previously unattainable. This section explores the distinctions between on-premises and cloud ERP systems, examines the benefits of cloud solutions, and highlights some leading providers in the market today.
Differences Between On-Premises and Cloud-Based ERP Systems
On-premises ERP systems require businesses to install and run the software on their own servers, providing full control but demanding significant upfront investments in hardware and maintenance. In contrast, cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on the vendor’s servers and accessed via the internet, offering a subscription model that generally results in lower initial costs and reduced IT overhead.
“Cloud ERP solutions enable access from anywhere, fostering a collaborative environment for teams across geographical boundaries.”
Advantages of Cloud ERP in Terms of Scalability and Flexibility
One of the most significant benefits of cloud ERP is its scalability, allowing organizations to easily adjust resources based on their current needs. Businesses can add or reduce users and functionalities without the complexities associated with on-premises systems. Additionally, cloud ERP solutions offer unparalleled flexibility, enabling access from any device with an internet connection. This flexibility supports remote work and can enhance productivity by providing real-time data and insights.
Popular Cloud ERP Providers in the Market Today
Several key players have established themselves as leaders in the cloud ERP space, offering robust solutions tailored to various industries. Here are a few notable examples:
- Oracle NetSuite: A comprehensive cloud ERP platform that integrates financials, CRM, and e-commerce, suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud: A next-generation suite that leverages intelligent technologies and analytics to provide real-time insights and business agility.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A flexible ERP solution that combines CRM capabilities with ERP functionality, designed to help businesses streamline operations and engage customers effectively.
- Infor CloudSuite: Industry-specific cloud solutions that focus on enhancing productivity and enabling businesses to respond swiftly to market changes.
Cloud technology continues to redefine how organizations approach ERP implementations, making it easier to adapt to the ever-evolving business environment. The move to cloud-based solutions not only fosters innovation but also provides businesses with the tools necessary to remain competitive in today’s market.
Future Trends in Enterprise Resource Planning Technology
As we look ahead, the landscape of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems is undergoing significant transformation. Emerging technologies are reshaping how businesses manage their resources, providing smarter and more efficient solutions. This section delves into key trends that are set to influence the future of ERP technology, including advancements in artificial intelligence, the rise of remote work capabilities, and the integration of machine learning.
Emerging Trends in ERP Technology
Several trends are on the horizon that promise to redefine ERP systems. These trends not only enhance functionality but also align with the evolving needs of modern businesses. The following points highlight these significant trends:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence: AI is being increasingly integrated into ERP systems, enabling automation of routine tasks, predictive analytics, and enhanced decision-making processes. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze past sales data to forecast future demand, allowing businesses to optimize inventory levels.
- Adoption of Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud technology is becoming a standard for ERP delivery. It offers scalability, cost efficiency, and remote accessibility, which are crucial for businesses aiming to adapt to changing market conditions quickly.
- Mobile ERP Applications: With the rise of mobile technology, ERP systems are evolving to provide mobile solutions that allow employees to access critical business data anywhere. This trend supports greater flexibility and responsiveness in business operations.
Implications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for ERP Systems
The incorporation of artificial intelligence and machine learning into ERP systems is revolutionizing how data is managed and utilized. AI and machine learning enhance ERP functionality by enabling advanced data analytics, which facilitates smarter decision-making.
“AI-driven ERP systems can automate data entry and provide real-time insights, reducing manual efforts and improving accuracy.”
These technologies allow for continuous learning from data, enabling systems to adapt over time. For example, a manufacturing company using AI-driven ERP can predict machinery failures before they happen, thus preventing downtime and saving costs. Additionally, machine learning algorithms enhance customer relationship management by analyzing customer behavior, allowing businesses to tailor their offerings effectively.
Potential of ERP Systems in Facilitating Remote Work and Collaboration
The shift towards remote work has accelerated the need for ERP systems that support collaboration across distributed teams. Modern ERP solutions are designed with features that enhance teamwork and communication, vital in a remote environment.These features include:
- Real-Time Data Access: Employees can access and update critical data from anywhere, facilitating seamless collaboration among team members, regardless of location.
- Integrated Communication Tools: Many ERP systems now offer built-in chat and video conferencing capabilities, allowing teams to communicate effectively while working remotely.
- Collaboration Platforms: Enhanced integration with project management and collaboration tools helps teams track progress, share documents, and manage tasks efficiently.
The potential of ERP systems in fostering remote work environments is substantial, especially as more organizations embrace hybrid work models. By leveraging these capabilities, businesses can maintain productivity and ensure that all employees remain connected and informed.
Customization vs. Standardization in ERP Systems
In the competitive landscape of business management, organizations face the crucial decision of whether to customize their Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems or to utilize standardized solutions. Customization allows businesses to tailor the system to their unique needs, while standardization offers efficiency and ease of use across the board. The choice between these two paths can significantly impact overall business processes and outcomes.Customization in ERP systems offers the flexibility to adapt the software according to specific business processes and unique industry requirements.
However, it also poses challenges such as higher costs, extended implementation timelines, and potential issues with system upgrades. On the other hand, standardized ERP solutions provide best practices and proven processes but may not fully align with the specific needs of every industry or organization.
Influence of Industry-Specific Requirements on ERP Customization
Industry-specific requirements play a pivotal role in determining the extent and nature of ERP customization. Different sectors have unique processes, regulatory needs, and customer expectations that standard ERP solutions may not adequately address. Therefore, organizations often opt for customization to ensure that their ERP systems align closely with their operational demands.
- Manufacturing Sector: In manufacturing, specific needs such as inventory management, supply chain tracking, and compliance with safety standards require tailored solutions. A manufacturing firm might customize its ERP to include specific modules for quality control and production scheduling, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Healthcare Industry: Healthcare organizations must adhere to strict regulatory standards and patient care guidelines. Customizing an ERP system to incorporate features like electronic health records (EHR) and patient tracking allows these organizations to meet compliance requirements while improving patient outcomes.
- Retail Sector: Retailers often require robust inventory management and point-of-sale (POS) systems. Customization can enable integration with online sales channels, customer loyalty programs, and dynamic pricing strategies, creating a seamless experience for both staff and customers.
Customization success stories abound across industries, demonstrating the tangible benefits of tailoring ERP solutions to meet specific needs. For example, a major automotive manufacturer implemented a customized ERP system to optimize its supply chain processes, resulting in a 20% reduction in operational costs and a significant improvement in delivery times. Similarly, a global healthcare provider successfully integrated a customized ERP solution that streamlined patient management, leading to enhanced care delivery and reduced administrative burdens.In contrast, some organizations that choose standardized ERP systems experience benefits such as quicker implementation and lower upfront costs.
However, they may find that their unique processes are not fully supported, potentially leading to inefficiencies in their operations. Therefore, the decision between customization and standardization should be driven by a careful analysis of both the current and future needs of the organization, balancing cost, efficiency, and the ability to meet industry standards.
“The choice between customization and standardization hinges on the specific operational demands of an organization and its industry.”
The Importance of Training and Support for ERP Users

Effective training and ongoing support are vital components in the successful implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. The significance of these elements cannot be overstated, as they directly influence how well users adapt to the new system and leverage its features to enhance productivity. When employees are well-trained, the overall return on investment (ROI) for ERP systems dramatically increases, leading to more streamlined operations and better data management.Training programs designed for ERP users serve to bridge the gap between system capabilities and user proficiency.
These programs must be tailored to meet the varying levels of experience among employees. A one-size-fits-all approach often leads to either insufficient knowledge or overwhelming information, making it crucial to utilize diverse training methods to cater to the needs of all users.
Methods for Delivering Effective Training
Various effective methods exist for delivering training to employees, ensuring they receive the knowledge necessary to utilize the ERP system efficiently. The following approaches can be incorporated into a comprehensive training strategy:
- Instructor-Led Training: Traditional classrooms, either in-person or virtual, allow for real-time interaction and personalized guidance. This method fosters a better understanding through direct engagement with trainers.
- Online Training Modules: Self-paced learning through e-learning platforms enables users to access training materials anytime, anywhere. This flexibility allows employees to learn at their own pace and revisit complex topics as needed.
- Hands-On Workshops: Practical sessions provide users with the opportunity to interact with the system in a controlled environment, allowing them to apply learned concepts and build confidence before going live.
- Peer-to-Peer Training: Encouraging experienced users to share their knowledge empowers teams and fosters collaboration, creating a supportive learning atmosphere.
- Simulation Exercises: Realistic practice scenarios can help users become familiar with the ERP system’s interface and functionalities, improving their ability to navigate the system effectively.
Ongoing support is equally crucial in maintaining ERP system efficiency. After initial training, users often encounter challenges that can hinder productivity if not addressed. A robust support system ensures that users have access to resources and assistance as they navigate the complexities of the ERP system.
Ongoing Support for ERP Users, Enterprise resource planning
The role of ongoing support in the success of an ERP system cannot be underestimated. Continuous support mechanisms should include:
- Help Desks: A dedicated help desk provides immediate assistance for technical issues, troubleshooting, and user inquiries, ensuring that problems are resolved swiftly.
- Regular System Updates: Keeping users informed about updates and new features allows them to take advantage of enhancements, improving overall system usage and efficiency.
- Feedback Loops: Establishing channels for users to provide feedback helps organizations identify areas for improvement and adapt training programs accordingly.
- Refresher Courses: Periodic training sessions to reinforce skills and introduce new features can keep users engaged and capable of utilizing the ERP system to its fullest potential.
- Community Forums: Online forums facilitate peer support, enabling users to share experiences, tips, and solutions, enhancing collective knowledge and support.
In summary, the importance of training and support for ERP users cannot be overlooked. Combining effective training methods with robust ongoing support ensures that employees are not only equipped to handle the ERP system but are also empowered to maximize its benefits in their everyday work.
Last Word
In summary, the journey of enterprise resource planning illustrates its crucial role in enhancing organizational efficiency and adapting to ever-changing market demands. As businesses continue to innovate and grow, ERP systems will undoubtedly evolve, incorporating new technologies and methodologies to meet the challenges ahead. Investing in robust ERP solutions can ultimately lead to increased productivity, better collaboration, and a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Essential Questionnaire
What is enterprise resource planning?
Enterprise resource planning is a type of software that organizations use to manage and integrate the important parts of their businesses.
How can ERP improve productivity?
ERP improves productivity by automating repetitive tasks, streamlining processes, and providing access to real-time data for better decision-making.
What industries benefit from ERP systems?
ERP systems are beneficial across a wide range of industries including manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and finance.
Is cloud ERP better than on-premises?
Cloud ERP offers advantages like scalability, remote access, and lower upfront costs, making it a popular choice for many businesses.
What challenges can arise during ERP implementation?
Common challenges include resistance to change, inadequate training, and integration issues with existing systems.